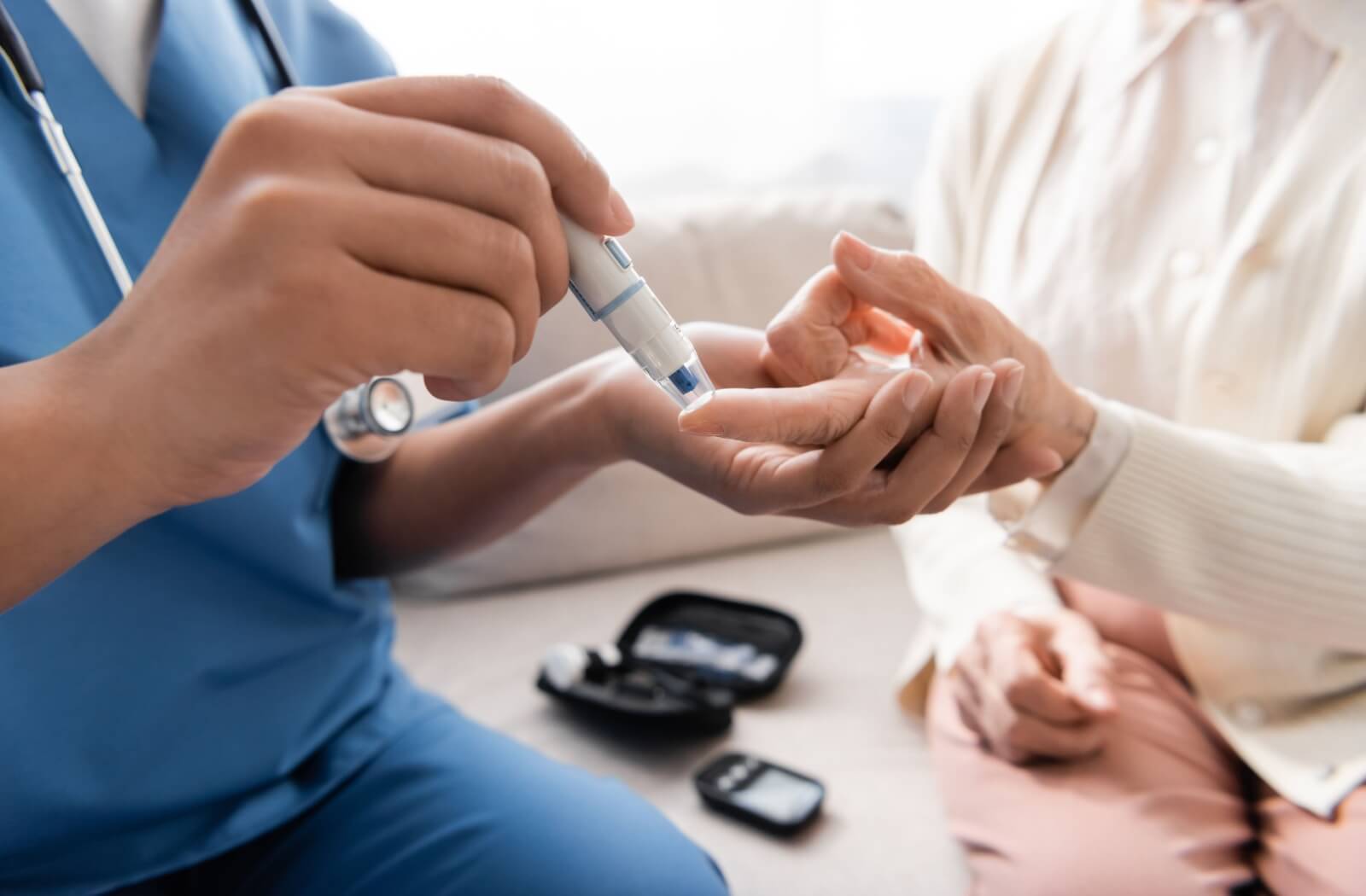
Caring for an elderly loved one with complex health and well-being needs such as diabetes can be a challenging, yet incredibly rewarding experience. Diabetes is a prevalent condition that requires careful attention and management to ensure quality of life for senior living.
For caregivers, understanding the nuances of diabetes management in older adults is crucial to providing effective care.
Understanding Diabetes in the Elderly
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, which, if not managed properly, can lead to complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and vision problems. In elderly patients, managing diabetes can be more complex due to the presence of other health conditions, medications, and age-related changes in the body. Here are a few factors caregivers should consider:
- Age-related Changes: Aging can affect how the body processes sugar and how it responds to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
- Medication Interactions: Older adults often take multiple medications, which may interact with diabetes treatments.
- Cognitive Impairment: Memory issues and cognitive decline can affect the ability to manage diabetes independently.
Essential Steps for Caregivers
Here are some comprehensive strategies to help manage diabetes effectively in elderly patients:
1. Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for managing diabetes effectively. Caring for an elderly person with diabetes involves:
- Checking Blood Sugar Levels: Use a glucometer to check blood sugar levels at recommended intervals. Pay attention to patterns and discuss any concerns with healthcare providers.
- Understanding Target Ranges: Know the target blood sugar ranges for your loved one, as these can differ based on age, health status, and individual risk factors.
2. Administer Medications Properly
Proper medication management is vital for keeping diabetes under control. Consider the following tips:
- Understand Medications: Ensure you know the purpose, dosage, and timing of each medication. Keep a record and update it with any changes.
- Watch for Side Effects: Be aware of potential side effects and interactions with other medications. Report any concerns to healthcare providers promptly.
- Assist with Insulin Administration: If insulin is required, learn how to administer it safely and accurately.
3. Encourage a Balanced Diet
Nutrition plays a significant role in diabetes management. Here’s how you can support healthy eating:
- Plan Balanced Meals: Focus on foods rich in fiber, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, while limiting sugary and high-fat foods.
- Monitor Portion Sizes: Help manage portion control to prevent overeating, which can lead to blood sugar spikes.
- Stay Hydrated: Encourage regular fluid intake to prevent dehydration, which can affect blood sugar levels.
4. Promote Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for managing diabetes and maintaining overall health:
- Encourage Safe Exercise: Activities should be suitable for their age and physical condition. Walking, swimming, or chair exercises are often ideal.
- Set Realistic Goals: Work with healthcare providers to set achievable activity goals tailored to their abilities.
- Supervise and Support: Provide supervision and assistance as needed to ensure safety during physical activities.
5. Manage Stress and Mental Health
Mental well-being is an important aspect of diabetes care:
- Identify Stress Triggers: Help identify and reduce sources of stress in their lives, as stress can affect blood sugar levels.
- Encourage Social Interaction: Social activities and interaction can improve mood and overall well-being.
- Offer Emotional Support: Provide emotional support and encourage open communication about their feelings and concerns.
6. Regular Healthcare Appointments
Keeping up with regular healthcare visits is crucial:
- Routine Check-Ups: Ensure regular check-ups with doctors, endocrinologists, and eye specialists to monitor diabetes and its potential complications.
- Coordinate Care: Coordinate with healthcare professionals to stay informed about treatment plans, updates, and any necessary adjustments.
7. Prepare for Emergencies
Be prepared to handle diabetes-related emergencies:
- Recognize Symptoms of Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar): Symptoms can include shakiness, sweating, confusion, and dizziness. Keep glucose tablets or a sugary snack handy.
- Know When to Seek Medical Help: Be aware of signs that require immediate medical attention, such as severe hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).

Building a Supportive Environment
Beyond managing the medical aspects of diabetes, creating a supportive environment is vital for older adults’ well-being:
- Educate Yourself and Others: Educate yourself and family members about diabetes to better understand your loved one’s needs.
- Adapt the Living Space: Make necessary adjustments to the home to ensure safety and accessibility, such as removing trip hazards and installing grab bars.
- Encourage Independence: Allow them to participate in their own care as much as possible, fostering a sense of independence and dignity.
Thinking About Assisted Living for Your Loved One?
Caring for an elderly loved one with diabetes requires patience, compassion, and dedication. By implementing these strategies, you can help manage diabetes effectively and improve their quality of life.
Remember, you’re not alone—seek support from healthcare providers, friends, and caregiver networks when needed. If you need more support or would like to learn more about the benefits of assisted living, contact Parsons House Austin. Our health-focused amenities, including a yoga studio, fitness classes, and an on-site walking track, are designed to help create a healthier, more fulfilling lifestyle for your loved one. We hope to see you soon!